Project Info
Category
Date
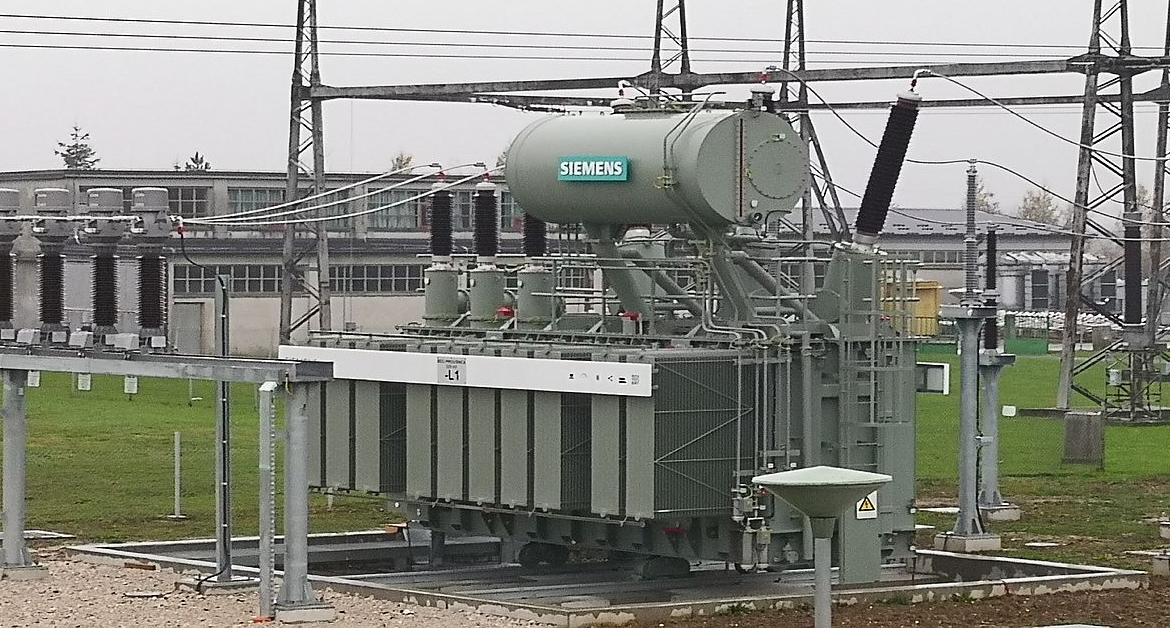
SHUNT REACTORS
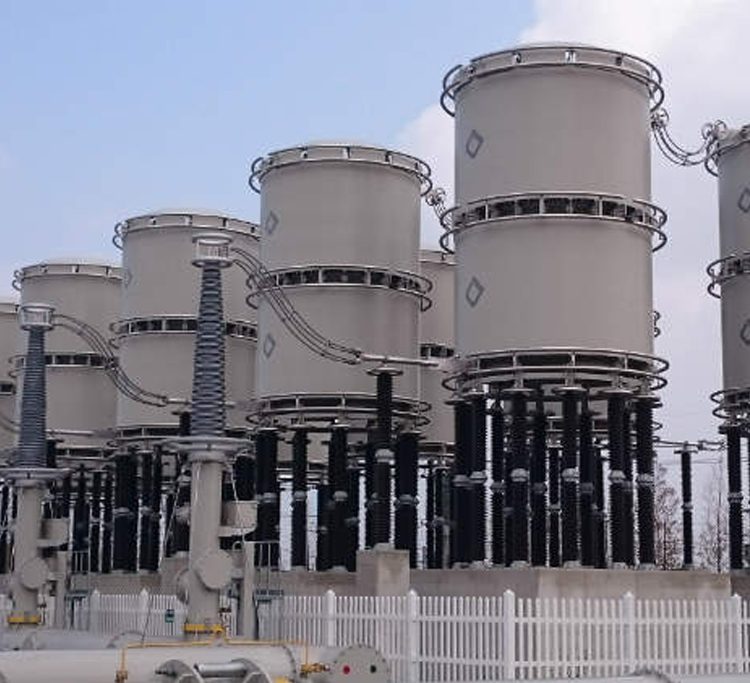
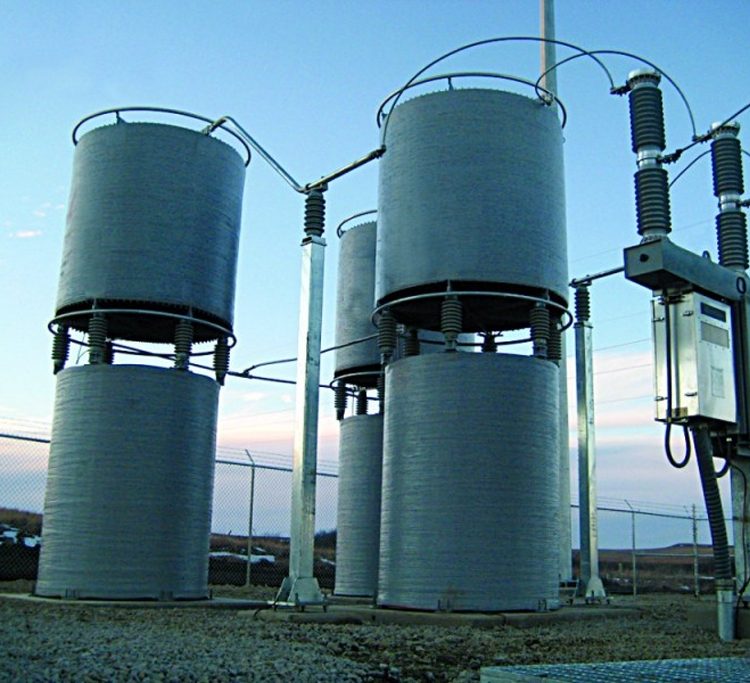
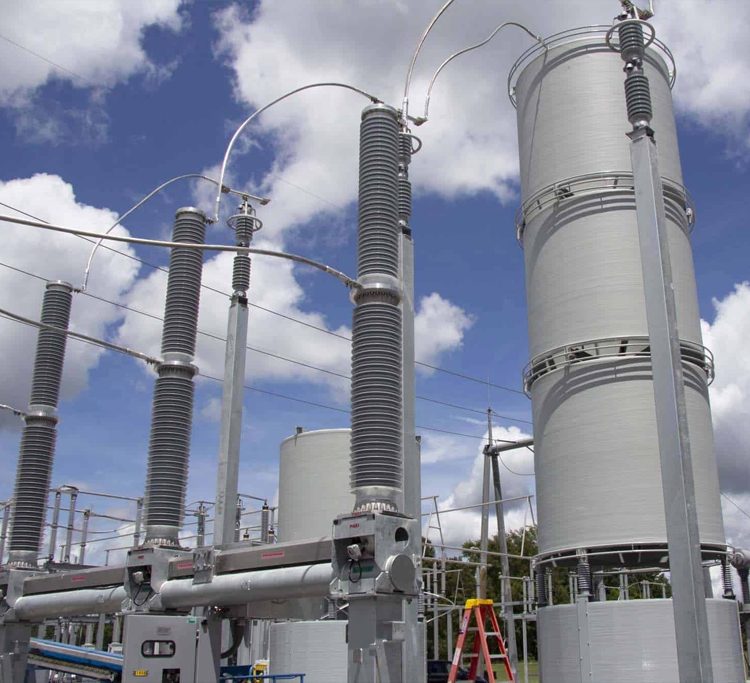



Features and Benefits:
1
Voltage Regulation:
Shunt reactors effectively stabilize voltage levels in transmission systems, particularly during periods of low load or when long transmission lines are energized.
2
Reactive Power Compensation:
By absorbing excess reactive power, shunt reactors help to prevent overvoltage conditions, reducing the risk of insulation failures and improving overall system reliability.
3
Improved System Efficiency:
They enhance the efficiency of power transmission by minimizing losses associated with reactive power flow, contributing to a more balanced load on the system.
4
Low Maintenance:
Designed for minimal maintenance requirements, shunt reactors provide reliable operation and reduced operational costs over their lifecycle.
5
Customizable Solutions:
Available in a range of configurations, our power transformers can be customized to meet specific customer requirements, ensuring optimal performance in various applications.
6
Low Noise Operation:
Designed for quiet operation, these transformers minimize noise pollution, making them suitable for urban installations and residential areas.
APPLICATIONS:
1
Transmission Systems:
Used in high-voltage transmission networks to improve voltage stability and manage reactive power flow.
2
Substations:
Installed at substations to regulate voltage levels and enhance the performance of transformers and other equipment.
3
Wind Farms and Solar Plants:
Employed in renewable energy installations to support grid stability by managing reactive power generated by intermittent sources.
4
Industrial Power Systems:
Utilized in large industrial facilities to maintain voltage levels and improve the efficiency of power distribution systems.
3
Long Transmission Lines:
Applied in long-distance transmission lines to mitigate the effects of voltage drops and ensure reliable energy delivery.
4
Commercial Buildings:
Suitable for large commercial complexes requiring efficient power distribution and management.